You have probably heard of this file before. But what exactly is behind the robots.txt file? How does it work and what effects does it have on your website?
We’ll tell you!
robots.txt – what is it?
A robots.txt file is a text file. It is a kind of instruction for bots and crawlers (e.g. Googlebot) that states which directories of a website may be read and which may not. For example, duplicate files can be excluded from indexing.
Without such a robots.txt file, the crawler or bot searches the entire website – potentially every single file. These can then all end up in Google search, for example, even if they shouldn’t end up there at all (e.g. private admin area of the website). This can also have a negative impact on your search engine optimization, as subpages are crawled that are not optimized for search engines.
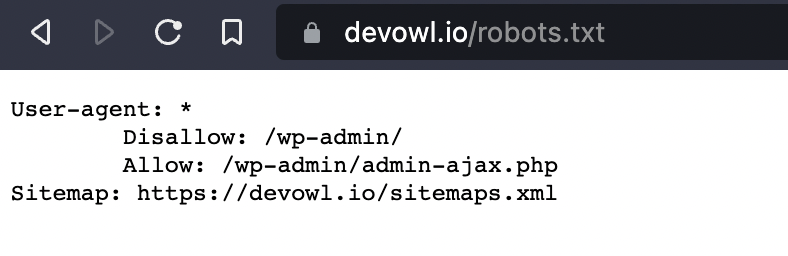
Example for a robots.txt file
In the screenshot you can see the txt file of the devowl.io website. In the following, we will break down the structure of the robots.txt file.
User-agent: *: This specifies which bots and crawlers are allowed to search the website. The asterisk (*) means that all bots/crawlers have access. Alternatively,User-agent:Googlebot could be entered here so that only the Google Bot searches the website.Disallow: /wp-admin/: In Disallow you define which directories, pages and files are not allowed to be read by the bots/crawlers defined in the user agent. In our case, these are pages that begin withdevowl.io/wp-admin/– i.e. the admin login. If instead of/wp-admin/there is simply /, this would mean that no directory may be searched. If you enter nothing afterDisallow:, all pages will be crawled.Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php: Allow all bots to search the specific PHP file. Again, the page name must match the one displayed in the browser.Sitemap: https://devowl.io/sitemaps.xml: In some cases – like ours – you will also find a sitemap entry in therobots.txtfile. This entry tells you where exactly you can find the sitemap of the corresponding website. You can copy the link and paste it into a new tab. All URLs of a website are listed in an XML sitemap.
Regular expressions in robots.txt
Sometimes it is impractical to always specify the full directory, page or file names. For example, if you want to exclude all .pdf files in all subdirectories from crawling. Therefore, there are regular expressions – dynamic rules – that you can use.
*: The*symbol – also known as a wildcard – is used when you want to have any characters within a string. For example, in disallow:/uploads/product/*/*.jpg, all JPG images (second asterisk for the image name) that are in a subdirectory (first asterisk) of uploads/product/ will no longer be crawled.$: There is also the dollar sign. This is used in addition to the wildcard symbol if you want to exclude URLs that have a certain ending. For example,disallow: *.pdf$says that all.pdffiles should not be crawled.
Crawl delay: Decide how fast the crawler works!
The crawl delay specifies the delay in seconds with which the bot should crawl the pages. Crawl delay: 10 means that the bot crawls at intervals of 10 seconds per file/page.
What a complex robots.txt file looks like
Theoretically, you can also expand your robots.txt file and include several entries. This could then look something like this:
User-Agent: GooglebotDisallow: /*.pdf$ User-Agent: Adsbot-Google Disallow: / User-Agent: * Disallow: /wp-admin/
In this example, the following happens:
- Google Bot: May crawl everything except
.pdffiles - Google Ads Bot: May not crawl the website at all
- All other bots: May crawl the entire website, except the
/wp-admin/directory.
Where can I find the robots.text file of my website?
The robots.txt file is located in the root directory of your website. You can access the file by calling up the domain of the website in your browser with the suffix /robots.txt. Example: devowl.io/robots.txt
In the same way, you will find the robots.txt file in the root directory when you connect to your webspace via FTP.
If a web crawler or bot wants to search your website, the robots.txt file in the root directory is its first port of call. After it knows what it is allowed to crawl in the first place, it searches the website further.
How can I create a robots.txt file?
In order to create a robots.txt file without much effort, there are now several tools that you can use. One of these tools is the robots.txt generator from ryte.
The robots.txt generator is very beginner-friendly. You can cobble together your robots.txt file in just a few steps. After you have set everything up, click on create and you can download the finished file. All you have to do is upload it to the root directory of your website, e.g. via FTP.
Another option is the robots.text generator from Small SEO Tools.
This generator is also similar to the one from ryte. You can make different settings – like defining the different bots. Then you can create and download the file.
How can I upload the robots.txt?
If you don’t want to upload the robots.txt file using an FTP client (e.g. Filezilla), you have two other options: Either you contact your hosting provider (if you do not have direct access to the web server) or you use a WordPress plugin. One of these plugins is WP Robots Txt.
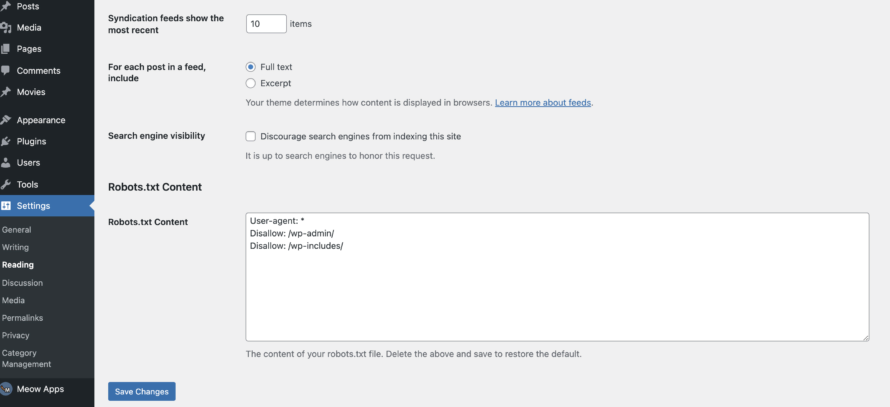
The plugin is free of charge. After installation, you will find it on the left in the menu bar under Settings > Reading. If you scroll down here, you will find the Robots.txt Content entry. Here, you can edit the robots.txt file in WordPress. You can enter the code we generated in the previous step in the corresponding field. Don’t forget to save the changes afterwards.
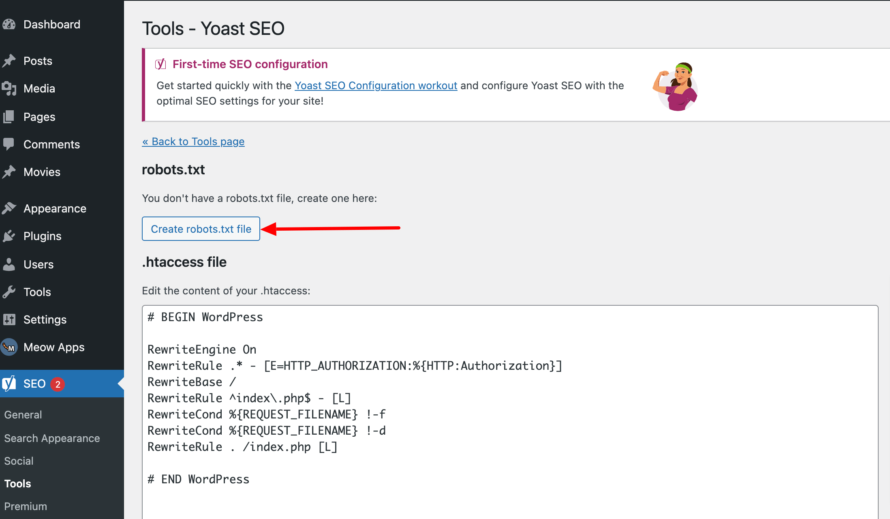
But you can also add a robots.txt file using the Yoast SEO plugin.
To import your created robots.txt file, go to Tools > File Editor in the menu on the left after installation. Here you will find the option to upload the file.
robots.txt and SEO
What does the robots.txt file actually have to do with search engine optimization? Not exactly a little. By means of the robots.txt file, you can basically better control which pages should be crawled and indexed by the bots. This not only saves Google time during crawling, but also helps to ensure that only relevant pages of your website end up in Google. This can have a positive influence on your Google ranking.